Zygoma Implant and Pterygoid Implant Role in Atrophic Maxilla
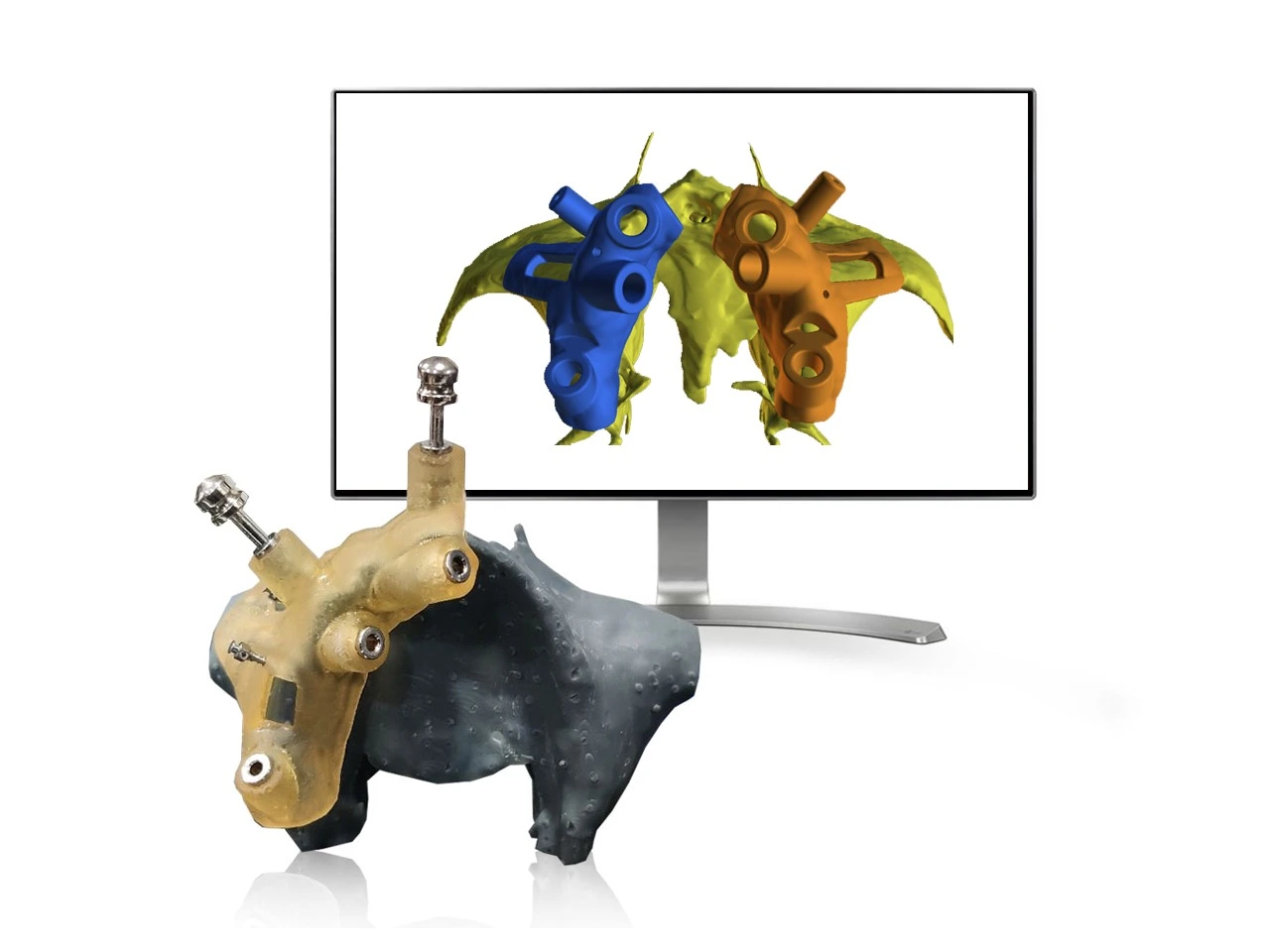

In the territory of maxillofacial surgery, atrophic maxilla poses significant challenges. Defined by a loss of bone volume in the upper jaw, it can severely impact facial aesthetics, oral function, and even psychological well-being. However, advancements in surgical techniques have led to innovative solutions, prominently involving the Zygoma and Pterygoid bones. In this blog, we delve into the pivotal roles of the Zygoma and Pterygoid in addressing atrophic maxilla cases, highlighting their anatomical significance, surgical implications, and therapeutic benefits.
Atrophic Maxilla
Before delving into the roles of Zygoma and Pterygoid, it's imperative to grasp the nature of atrophic maxilla. This condition arises due to various factors, including tooth loss, periodontal disease, trauma, or congenital defects, leading to reabsorption of the alveolar ridge and subsequent bone loss. As a consequence, traditional dental implant placement becomes challenging, necessitating alternative approaches to restore function and aesthetics.
The Zygoma: A Structural Pillar
The zygoma, or cheekbone, serves as a critical anatomical landmark in facial structure. Its robust nature and strategic positioning make it an ideal candidate for supporting dental implants in cases of severe maxillary atrophy. Zygoma implants, pioneered by Branemark in the 1990s, anchor directly into the zygomatic bone, bypassing the deficient maxillary ridge.
Zygoma Implant Technique and Considerations
Zygoma implant placement requires meticulous planning and surgical expertise. Guided Implant planning with Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging aids in preoperative assessment and planning, facilitating precise determination of zygoma anatomy and bone density. Surgical access typically involves a lateral approach, necessitating careful avoidance of vital structures such as the infraorbital nerve and maxillary sinus.
Therapeutic Advantages
Zygoma implants offer several therapeutic advantages in atrophic maxilla cases. By bypassing the need for extensive bone augmentation procedures, they reduce surgical complexity and overall treatment duration. Moreover, their anchorage in dense zygomatic bone provides exceptional stability, enabling immediate loading protocols in select cases, thereby expediting functional restoration and patient satisfaction.
The Pterygoid: An Intricate Support System
Adjacent to the zygoma lies another crucial structure, the pterygoid bone. Comprising the medial and lateral pterygoid plates, it contributes to the structural integrity of the maxilla and serves as a secondary anchorage site for implants in atrophic cases.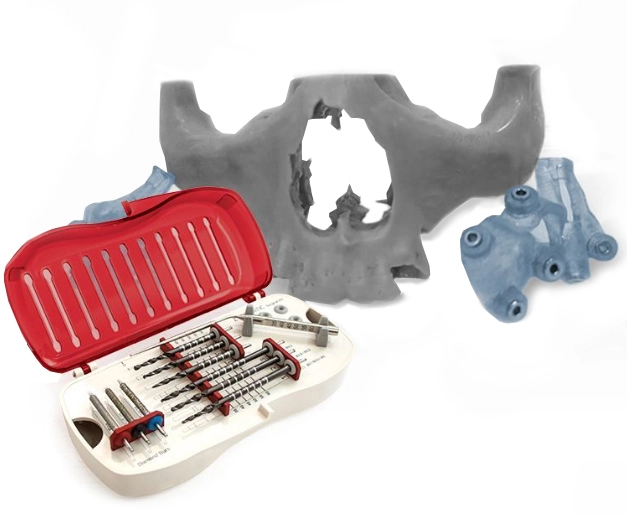
Utilizing the Pterygoid in Implantology
In cases where zygomatic bone quality or quantity is insufficient, the pterygoid region offers an alternative site for implant placement. Transzygomatic or zygomatico-pterygoid implants traverse through the zygoma into the pterygoid region, enhancing stability and support. Additionally, the pterygoid implants can be combined with conventional implants in a hybrid approach, further optimizing outcomes.
Pterygoid implant Nuances and Challenges
Pterygoid implants placement necessitates precise surgical technique and thorough anatomical knowledge. Careful attention must be paid to avoid injury to critical structures such as the internal maxillary artery and the pterygopalatine fossa. Moreover, thorough preoperative evaluation is crucial to assess bone quality and ensure adequate implant anchorage.
Therapeutic Benefits and Considerations
Pterygoid implants offer unique therapeutic benefits in atrophic maxilla cases. By distributing occlusal forces along the posterior maxilla, they enhance biomechanical stability and minimize the risk of implant failure. Furthermore, their utilization reduces the need for extensive bone grafting procedures, streamlining treatment and improving patient outcomes.
Surgical Guided Dental Implant
Guided digital dental implant planning has revolutionized the field of maxillofacial surgery, particularly in addressing atrophic maxilla cases involving zygoma and pterygoid utilization. By leveraging advanced imaging modalities such as CBCT scans and intraoral scans, we can precisely map out the patient's anatomy in three dimensions. This enables virtual implant placement with meticulous attention to detail, ensuring optimal positioning and angulation for zygomatic and pterygoid implants. Moreover, guided surgical templates fabricated based on digital plans serve as invaluable tools during the actual procedure, facilitating accurate implant placement with minimal invasiveness. Through this innovative approach, guided digital dental implant planning enhances the safety, predictability, and overall success of zygoma and pterygoid-based interventions, ultimately benefiting patients with atrophic maxilla conditions.
Conclusion
The zygoma and pterygoid bones emerge as indispensable allies in the surgical management of atrophic maxilla cases. Through innovative techniques such as preoperative guided implantology endorsing strategic implant placement, these anatomical structures offer effective solutions for restoring oral function and facial aesthetics in patients with severe bone loss. As technology advances and surgical expertise evolves, the role of zygoma and pterygoid in maxillofacial surgery continues to expand, promising brighter prospects for patients facing the challenges of atrophic maxilla.
DOWNLOAD FREE E-BOOK
Kick start your Guided Surgery Practice.
 USA & Canada:
USA & Canada:
 UK:
UK:

Comments: